Medical and nursing schools now routinely use simulators to train students in medical procedures. Learn how simulation is used in medical training and research here.
Medical Education and Training
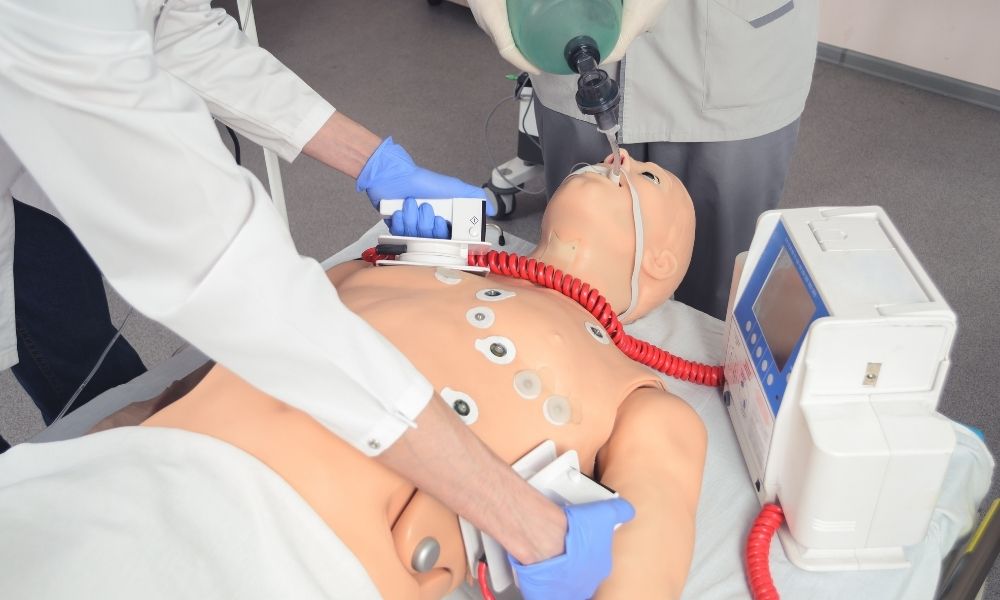
The days of using citrus fruit to practice injections have been replaced by robotic medical mannikins. These dummies can be programmed by computers to behave as real patients would when suffering from different medical emergencies or conditions that require medical intervention. Students can practice what to do when a patient has a heart attack, stops breathing, or undergoes a life-threatening reaction to drugs.
Medical mannikins can simulate broken bones or provide practice for inserting intravenous lines or catheters. These mannikins can simulate human pulse, respiration, and other vital signs. Clinical simulations using smart mannikins allow students to practice medical skills and techniques and learn from mistakes without endangering live patients.
In addition to plastic mannikins, medical training now makes use of virtual and augmented reality. The former is a completely artificial environment that’s provided digitally through special goggles, while the latter uses digital overlays to reveal the position and condition of internal organs.
Doctors and nurses in training can also use computer simulations to practice communication skills by role-playing with digital representations of patients. These online avatars are programmed to react with realistic human emotions during conversations with medical professionals.
Medical Research
Advances in medical diagnostic device designs have resulted in the development of a technology called “Organ on a Chip” or OOAC. Microfluidic devices direct body fluids or cell samples along micro-channels to interact with chemical reagents or drugs.
These devices may one day eliminate the necessity of animal testing and make clinical tests of new drugs safer for patients by identifying potential toxicity before trials proceed. Groups of OOAC devices can be connected to each other to mimic the behavior of some human organs. Devices under development include integrated chips that can communicate data about the results of the simulation occurring on the chip.
The future of simulation in medical training and research includes expanded use of artificial intelligence and devices that can adapt to student learning styles and skill levels.